本文已被:浏览 2073次 下载 4559次
投稿时间:2018-03-27 修订日期:2018-04-03
投稿时间:2018-03-27 修订日期:2018-04-03
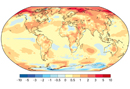
中文摘要: 2017年全球主要温室气体浓度继续攀升,地表温度相比工业化前水平高出1.1℃,位列2016年之后,为有气象观测记录以来的历史第二高值,也是有记录以来最暖的非厄尔尼诺年份。全球冰冻圈持续萎缩,冬季北极最大海冰范围创历史新低,南极海冰范围全年处于历史低位。全球海表面温度显著高于常年,海平面持续上升,海洋热含量创历史新高,海洋酸化的影响持续加剧。世界各地发生了许多重大天气气候事件,包括异常活跃的北大西洋飓风、印度次大陆的季风洪水、东非部分地区的持续干旱,以及全球多地的暴雨洪涝、高温热浪、低温寒流和强对流天气,2017年成为有记录以来气象灾害造成经济损失最大的年份。本文总结了2017年全球重大天气气候事件及其影响,并重点分析了大西洋飓风季异常活跃和美国西海岸高温热浪天气两个典型事件的形成原因。分析表明,8月底至10月初,加勒比海和热带西大西洋海温偏高,对流活动旺盛,风速垂直切变偏小,为飓风的发展加强提供了有利的背景条件,加之北美副热带高压出现阶段性减弱,导致4个强飓风接连登陆美国和加勒比海地区;7月上旬,受副热带西风急流加强东伸,东北太平洋切断低压维持影响,北美副热带高压持续控制美国西南部地区,是当地高温热浪事件发生的主要原因。
中文关键词: 表面温度,降水量,极端事件,气象灾害
Abstract:The concentration of greenhouse gases continued to increase in 2017, and the global mean temperature was 1.1℃ above the pre-industrial levels, making the year 2017 become the second warmest year on record and the warmest year not influenced by El Nino event. The cryosphere continued its contraction. The maximum sea-ice extent of Arctic sea in winter broke the lowest record while the sea-ice extent of Antarctic was near the record low level throughout the year. Global sea surface temperatures were significantly above the 1981-2010 average, and the global mean sea level kept rising steadily. The ocean heat content reached new record highs due to the intensified impact of ocean acidification. Many significant weather and climate events occurred in 2017, including a very active North Atlantic hurricane season, major monsoon floods in the Indian subcontinent, severe droughts in East Africa as well as some torrential rains, heat waves, cold waves and severe convective weather at regional or local scale worldwide. Econo-mic losses from the weather and climate related disasters set a new record in 2017. This paper summarizes the major events and its impact in 2017, and analyzes the formation causes of typical events including the exceptionally destructive hurricanes that occurred in rapid succession in the North Atlantic and the significant summer heat waves in the United States. Analysis of atmospheric circulation and external forcing shows that the positive SST anomalies of Caribbean and western tropical Atlantic enhanced the convective activity and decreased the vertical shear of wind speed, providing favorable background conditions for the development of hurricanes. In addition, the stage weakening of North American subtropical high caused four destructive hurricanes to make landfall successively in southern United States and the Caribbean region. In early July, the North American subtropical high that was influenced by the eastward extension and enhancement of subtropical westerly jet and the maintaining of Northeast Pacific cut-off low continued controlling the southwestern United States. This was the major reason for the summer heat wave on the west coast of the United States.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(41701103)和公益性行业(气象)科研专项(GYHY201506002)共同资助
| 作者 | 单位 |
| 孙劭 | 1. 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081 2. 中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081 |
| 王东阡 | 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081 |
| 尹宜舟 | 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081 |
| 王国复 | 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081 |
| 柯宗建 | 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081 |
引用文本:
孙劭,王东阡,尹宜舟,王国复,柯宗建,2018.2017年全球重大天气气候事件及其成因[J].气象,44(4):556-564.
SUN Shao,WANG Dongqian,YIN Yizhou,WANG Guofu,KE Zongjian,2018.Global Major Weather and Climate Events in 2017 and the Possible Causes[J].Meteor Mon,44(4):556-564.
孙劭,王东阡,尹宜舟,王国复,柯宗建,2018.2017年全球重大天气气候事件及其成因[J].气象,44(4):556-564.
SUN Shao,WANG Dongqian,YIN Yizhou,WANG Guofu,KE Zongjian,2018.Global Major Weather and Climate Events in 2017 and the Possible Causes[J].Meteor Mon,44(4):556-564.