本文已被:浏览 1161次 下载 3480次
投稿时间:2017-04-12 修订日期:2018-10-08
投稿时间:2017-04-12 修订日期:2018-10-08
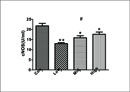
中文摘要: 为了探讨短时高浓度与相对长时间低浓度下不同的PM2.5污染过程对小鼠急性氧化应激及炎症反应的不同影响,将48只雄性C57BL/6小鼠按体重随机分为6组(n=6),使用人工气候环境暴露仓模拟不同的PM2.5污染过程,分别给予轻度污染组(PM2.5平均浓度为100 μg·m-3)连续暴露72 h,中度污染组(PM2.5平均浓度为150 μg·m-3),连续暴露48 h,重度污染组(PM2.5平均浓度为250 μg·m-3)连续暴露28.8 h;每组设置空白对照组。暴露染毒结束后,采用试剂盒法测定C反应蛋白(CRP)、结构性一氧化氮合酶(cNOS)、同型半胱氨酸(HCY)、白介素8(IL8)。低浓度长时间的PM2.5暴露组的CRP、cNOS、IL8水平显著高于高浓度短时间暴露组,差异性具有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01),cNOS的抑制水平为低浓度长时间组显著高于高浓度短时间组,差异性具有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。结论:相同暴露剂量下PM2.5轻度污染持续72 h的健康损害比PM2.5重度污染持续28.8 h的对健康损害更大, PM2.5中度污染持续48 h的健康损害次之,应重视长时间轻、中度污染对人体健康的影响,适当调整空气质量的预警标准。
中文关键词: 暴露差异性,PM2.5,健康风险,炎症反应,抗氧化能力
Abstract:This paper is to explore the different anti oxidant and inflammation effects of short time high dose and long time low dose fine particular matter (PM2.5) on rats. Forty eight healthy male C57BL/6 rats were randomly divided into six groups, eight in each. Low dose group, moderate dose group and high dose group were exposed to PM2.5at 100 μg·m-3, 150 μg·m-3 and 250 μg·m-3 on average, respectively, using the artificial climate environment expose cabinet. 〖JP2〗Meanwhile, three blank 〖JP〗groups were also set. After exposure, C reactive protein (CRP), constructivenitric oxide synthase (cNOS), homocysteine (HCY), interleukin8 (IL 8) were analyzed. The results showed that the levels of CRP, HCY and IL 8 in long term low dose group are significantly higher than those in the short term 〖JP2〗high dose group (P<0.05, P<0.01). 〖JP〗The inhibition level of cNOS in the low dose group is also significantly higher than that in the short term high dose group (P<0.05, P<0.01). The ranking of PM2.5 exposure to health damage effect is low dose 72 h, moderate dose 48 h and high dose 28.8 h when the PM2.5 exposure dose is same.
文章编号: 中图分类号: 文献标志码:
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(416750111)和上海市气象局科技开发面上项目(MS201411)共同资助
引用文本:
周骥,孙庆华,许建明,彭丽,叶晓芳,杨丹丹,2018.上海地区不同PM2.5污染过程对炎症应激影响的差异性[J].气象,44(12):1612-1617.
ZHOU Ji,SUN Qinghua,XU Jianming,PENG Li,YE Xiaofang,YANG Dandan,2018.Effects of Different PM2.5 Pollution Processes on Inflammatory Stress in Shanghai Area[J].Meteor Mon,44(12):1612-1617.
周骥,孙庆华,许建明,彭丽,叶晓芳,杨丹丹,2018.上海地区不同PM2.5污染过程对炎症应激影响的差异性[J].气象,44(12):1612-1617.
ZHOU Ji,SUN Qinghua,XU Jianming,PENG Li,YE Xiaofang,YANG Dandan,2018.Effects of Different PM2.5 Pollution Processes on Inflammatory Stress in Shanghai Area[J].Meteor Mon,44(12):1612-1617.